A Kalamazoo College alumna is among the people playing important roles in the fight against Parkinson’s disease (PD) at The Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research (MJFF), headquartered in New York City.
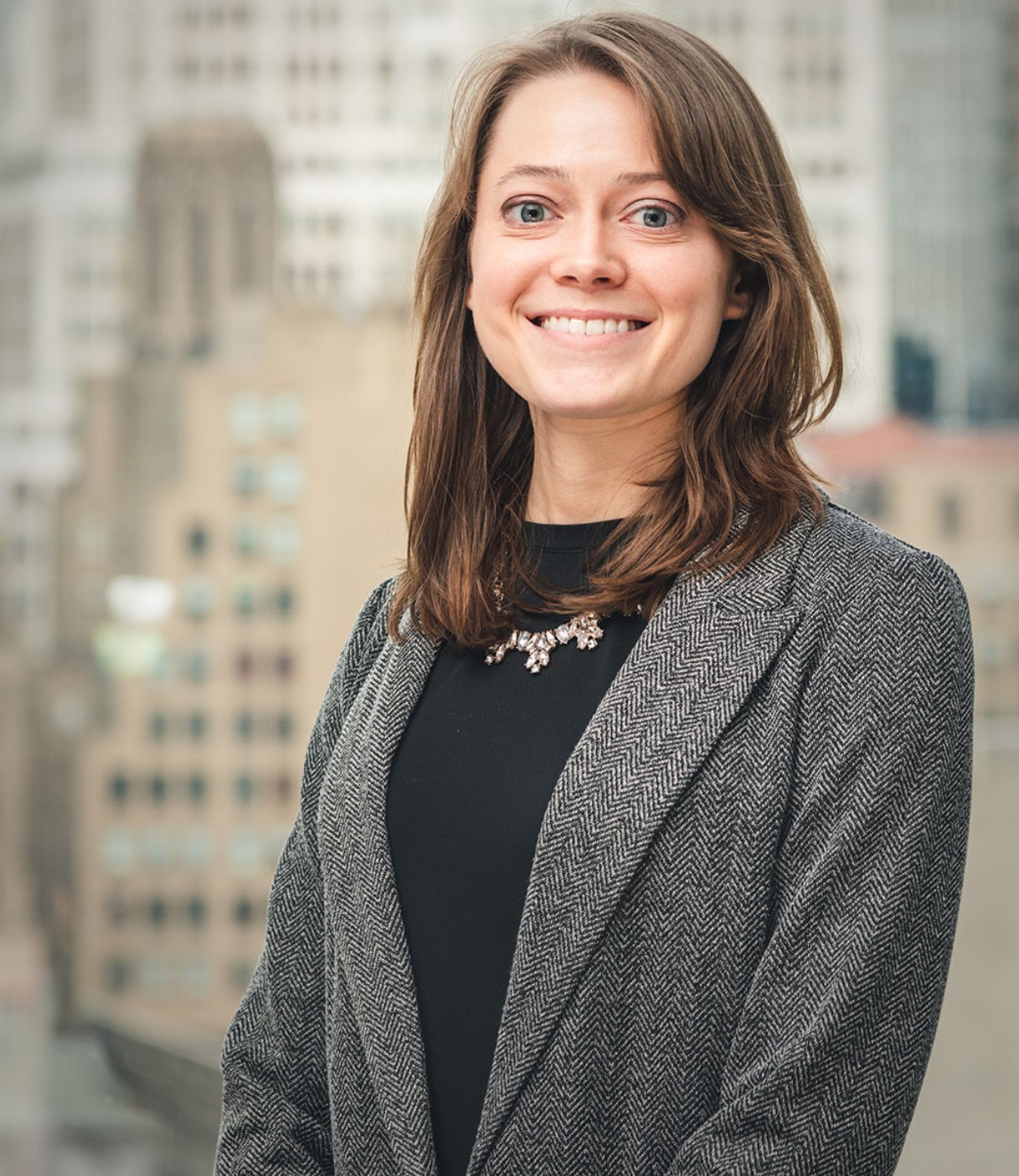
The foundation, which launched in 2000, says it’s dedicated to finding a cure for PD—a progressive chronic neurological movement disorder—through an aggressive research agenda that also ensures the development of improved therapies for those living with the disease today. As the organization’s director of research resources, Nicole Polinski, Ph.D. ’12 ensures that industry and academic researchers have access to the biology tools—called reagents—and preclinical models that they need for performing biology and chemistry experiments.
High-quality research tools are vital for successful, reproducible science. MJFF’s Research Tools Program team, including Polinkski, works with the research community to understand the gaps in the research tool space, develop and distribute reagents and models to fill these gaps, and better understand the characteristics of available research tools.
“I think my biggest challenge is to make sure that our limited resources have the biggest impact possible,” Polinski said. “It’s trying to identify what we need as we get suggestions for where we should focus our laboratory-tool development. It’s trying to connect the dots between different things you’re hearing from different folks to make sure that we prioritize and select the programs that have the potential to impact a lot of labs. Figuring out what to prioritize and who to work with on those programs.”
The early signs of Parkinson’s disease include tremors, often in the hands or fingers; a loss of smell; trouble moving or walking, including stiffness and balance problems; constipation; a reduction of facial expressions; dizziness or fainting; sleeping problems and stooping or hunching over. Polinski said Parkinson’s is diagnosed through such traditional motor systems, but until recently, it’s pathology could only be confirmed at autopsy. As a result, misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis is still all too common.
“The two pathological hallmarks that are confirmed in an autopsy are in the brain,” Polinski said. “One is the presence of a protein that’s normally in the brain, but it starts to clump abnormally with Parkinson’s. It’s the presence of those clumps and then the loss of a specific brain system, which consists of a circuit that deals with movement.”
Research, though, through MJFF and its partners, is beginning to provide more methods for diagnosis as well as treatment.

National Parkinson’s Awareness Month
April is Parkinson’s Disease Awareness Month. Organizations such as The Michael J. Fox Foundation, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, and the American Parkinson Disease Association host events and campaigns, provide resources for people living with Parkinson’s, and support research efforts in the fight against the ailment, which afflicts more than 10 million people worldwide including about 1 million in the U.S.
In 2023, an international coalition of scientists led by MJFF discovered a Parkinson’s biomarker—a tool that can detect the earliest biological signs of the disease in living people.
“We need better ways to diagnose it, and I think we’re making good headway,” Polinski said. “There’s now a test with cerebrospinal fluid that can detect those clumps. It’s still not perfect. A lumbar puncture to collect the fluid is not easy. Hopefully, we might be able to use saliva and blood or other bodily fluids that require less invasive procedures in the future.”
Michael J. Fox is widely known as an actor for his role as Alex P. Keaton on the 1980s situation comedy Family Ties. He later became a movie star with roles in Teen Wolf, Back to the Future, The Secret of My Success and Casualties of War. In 1991, Fox developed a tremor in his pinky finger. He consulted a neurologist and was diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease at just 29 years old. Still, he found a way to channel that life-changing news into a way to help others.
“I’ve met Michael a number of times and he came to our all-staff meeting earlier this year for a fireside chat,” Polinski said. “He talked about his experience and where he’s at now. You know how he feels about the work and all that the foundation he established has accomplished. It’s always great to see him. He’s as nice as he is portrayed.”
In her early years at K, Polinski knew she wanted to major in biology, but no one in her family had a science background, and her exposure to the medical field was primarily through medical doctors. She assumed she would also go to medical school and become a physician herself until she started her Senior Integrated Project (SIP).
“I ended up doing a summer internship at a spinal cord injury lab at The Ohio State University and I really liked being in the lab,” Polinski said. “After that, I started looking more into graduate schools and went on to get a Ph.D. in neuroscience.”
Shortly after graduate school at Michigan State University, she began working for The Michael J. Fox Foundation as a research program officer, advancing to associate director and senior associate director before earning her current position. It’s a role she relishes, knowing her work contributes to an important fight.
“We’re well on our way to improving ways to diagnose Parkinson’s disease with some recent breakthroughs, and we have more diverse therapeutic strategies in testing than ever before,” Polinski said. “On top of that, we’re identifying new pathways to tackle Parkinson’s disease by looking at patient bio samples to better understand the disease at a basic biological level. I’ve been here almost nine years, and no two days ever look the same. It’s a field that is ever evolving, and even within my laboratory tools space, new technologies and targets are popping up that need support with new players in the field. It’s something that’s always changing, and I really enjoy that challenging feature of this work. I never get bored, and I love my job.”