in “Points of Return,” an online exhibit dedicated to climate change.
An online art exhibit dedicated to pushing for action against climate change while there’s still hope for the planet features two artists with Kalamazoo College connections.
Jo-Ann and Robert Stewart Professor of Art Tom Rice and alumna Bethany Johnson ’07 were among the 25 international artists chosen from more than 300 entrants for “Points of Return.” The exhibit focuses on the harm humans have caused to the Earth, particularly since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution, while emphasizing there are still multiple paths and approaches that can be taken to restore an environmental balance.
“Points of Return” is presented by A La Luz, which translates from Spanish as “spotlight” or “to shed light on.” The group was founded in 2015 by environmental artists David Cass and Gonzaga Gómez-Cortázar Romero to be a wide-ranging platform for sustainable and environmentally focused creative work. The exhibit unfolds across six sections, defined as viewing rooms, that describe a movement that comes full circle through planetary ecosystems, art disciplines and mediums.

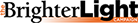
such as chipboard, foam, hardboard, paper, plastic, plexiglass, particleboard,
plywood and wood in “Safe Keeping,” which deals with material consumption
and the resulting pollution, climate change and landfill waste.
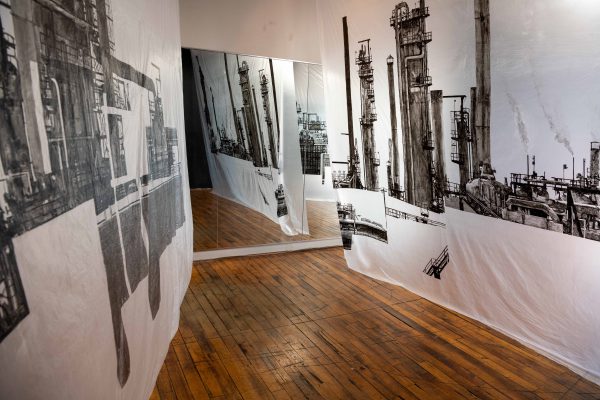
Rice’s part of the exhibit shows one of his projects, “Precarious Living,” within the work he pursued for four months as a Fulbright Canada research chair in arts and humanities at the University of Alberta. There, he exhibited a climate-themed installation titled “Shifting Uncertainties: The Land We Live On.”
“‘Points of Return’ represents artists from many different parts of the world, which is important because climate change is a global issue,” Rice said while calling his selection to the global exhibit an honor. “What we do locally or nationally impacts areas of the world that contribute much less to the climate crisis. The online format of the exhibition ensures that many more people will have the opportunity to spend time with the artwork than if it had been a physical exhibition. Accessibility to information is critical to changing people’s minds and behaviors related to climate-change issues.”
Rice used an Alberta-area oil refinery as the main visual resource for “Precarious Living.”
“I hope that my work will help people be self-reflective and ask questions about the climate crisis,” Rice said. “‘Precarious Living’ is a large-scale drawing installation that poses more questions than it answers. The subject matter is focused on an oil refinery made up of a mass of pipes, upgraders, holding tanks, chimineas and flares that amount to an absurd maze of fragile connections. What is really going on here? How can we comprehend the impact of an industry that is the very foundation of our economy, but threatens our very existence? The drawings have large sections of redacted information. For me, these redacted or negated elements represent both subterfuge by the fossil fuel industries, and our own self-imposed delusion that we can continue burning fossil fuels and that technology will save us. ‘Precarious Living’ is about being at the tipping point of global warming.”
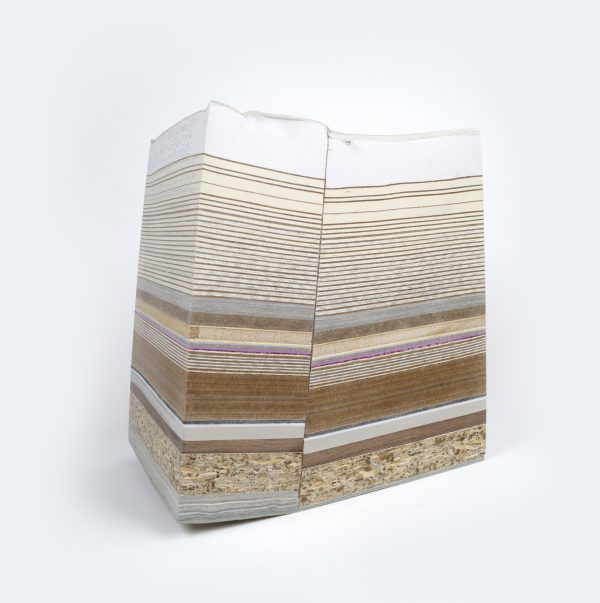
Johnson’s artwork is represented by Moody Gallery in Houston, Texas, and she is an Assistant Professor in the School of Art and Design at Texas State University. Her work in “Points of Return,” titled “Safe Keeping,” deals with material consumption and the resulting pollution, climate change and landfill waste. She feels those are important issues for artists to face given the work they pursue and how they pursue it.
“I think there can be an attitude in the art world that one’s conceptual ideas must be realized by any means possible; that essentially, the scale, media and production methods must inherently follow from the artist’s greater conceptual idea,” Johnson said. “This can lead to an incredible amount of material consumption, energy use, and the utilization of toxic, unsustainable materials within the art world. Under the current conditions of our climate crisis, I feel that the art world is in desperate need of material and energy ethics; that we think seriously about the impacts of our work on the environment, and strive toward artmaking practices that are renewable, environmentally sensitive and even climate positive in their impacts.”
In line with the overall exhibition, Johnson’s display embodies anxiety and hope along with grief and joy as she uses layered materials that are reminiscent of geological core samples, land formations and geological processes. Her materials include paper, plastic, foil food wrappers, aluminum and foam that bring new life to discarded waste.
“I hope to offer an opportunity for discussion and reflection on the issues of human consumption and material waste, while also generating works that are entrancing and poetic, independently from their environmental themes,” Johnson said. “In this way, my goal is for them to contain ‘layers’ of meaning, which hopefully allows them to reach a wide audience in different ways.”
Johnson said she doesn’t blame artists—or any individuals for that matter—for the climate emergency as the problems that contribute to it are systemic, and intrinsic to capitalism, energy systems and powerful corporations. However, individuals must grapple with the results of it.
“This is where I think we can all recapture some power from that system by mindfully adopting ethical, responsible and sustainable models of living and working,” she said. “It can be, at its best, a hopeful, even joyful, act of resistance and psychic repair.”
Johnson feels that individuals who stay politically active can have great power against climate change and environmental problems by acting locally when they act together.
“Much environmental policy and action happens at levels beyond the individual, so voting and getting involved with local and regional politics can be hugely impactful,” she said. “For example, I live in a neighborhood in Austin, Texas, that used to house several environmentally toxic commercial facilities where oil had been leaching into the ground for years. A small group of concerned neighbors spent many years advocating for the cleanup and environmental remediation of these sites, and were eventually successful. The fact that I can live here with a sense of safety for my own health is thanks to a dedicated group of people working on a specific, concrete goal. Both in terms of the actual environmental impact as well as the sense of personal agency that it can create, I think finding a specific, actionable and realistic goal on a local level can have a great impact.”
Rice agrees that the collective actions of individuals are likely to be beneficial.
“Timothy Morton asks in his book Hyperobjects: Philosophy and Ecology After the End of the World, ‘does my driving a Prius or recycling my plastic bottles really help,’” Rice said. “I think the answer is no, of course not, but that doesn’t mean it isn’t important to do those things. I think it was Elizabeth Kolbert in The Sixth Extinction who points out it will take mass social movements to create real change related to the climate crisis. Social change happens a person at a time. Individually, we can’t initiate real change, but we are part of a larger network. What we do individually matters.”